Describe the Role of the Cochlea in Hearing
The cochlea is capable of exceptional sound analysis in terms of both frequency and intensity. Despite its name a cochlear implant does not restore normal hearing.
/Ear-GettyImages-586038190-42999e6443b441d5876c5e3c5dd640cf.jpg)
Cochlea Anatomy Function And Treatment
Sound waves are transduced into electrical impulses that the brain can interpret as.
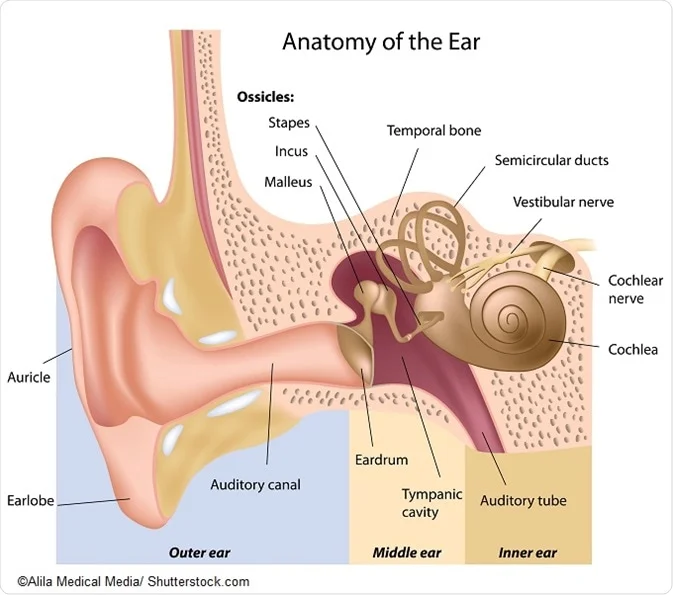
. The cochlea contains the sensory organ of hearing. The cochlea auditory inner ear transforms the sound in neural message. Cochlea is the auditory organ present in the inner ear.
The inner ear is a maze of tubes and passages referred to as the labyrinth. In the cochlea It transforms sound waves into electrical impulses which are sent on to the brain. This movement pushes on fluid found in the cochlea of the inner ear.
So remeber from vibration to liquid. Auditory receptors are present in the cochlea. Loud or soft high or low short or long etc to the brain where different structures work together to create a.
Lelu 443 5 months ago. The cochlea is the auditory center of the inner ear a fluid-filled organ that translates the vibrations of auditory sound into impulses the brain can understand. Cochlea Structure of the cochlea.
It stimulates the auditory nerve to give people who are deaf or have severe hearing loss a representation of different sounds and help them to understand speech. Sound is captured by the outer ear amplified by the middle ear and transferred to the inner ear or cochlea which transforms the sound vibration into a neural signal. It bears a striking resemblance to the shell of a snail and in fact takes its name from the Greek word for this object.
The cochlea is a hollow spiral-shaped bone found in the inner ear that plays a key role in the sense of hearing and participates in the process of auditory transduction. The cochlea auditory inner ear transforms the sound in neural message. The movements of the fluid in the cochlea bend the hair cells of the inner ear much in the same way that a gust of wind bends over wheat stalks in a field.
Hearing aids incorporating com pression can help to compensate for the effects of reduced dynamic range. What is the role of the cochlea in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth in humans making 275 turns around its axis the modiolus.
The cochlea is filled with special fluids which are important to the process of hearing. In the ear the cochlea is the snail-shaped structure responsible for transferring pressure waves into nerve impulses. The cochlea is a fluid-filled tube that converts vibrations into nerve impulses.
While the external and middle ears are mainly concerned with the transmission of sound the inner ear contains the cochlea often called the organ of hearing and also houses the bodys organ of balance. The movements of the hair cells trigger nerve impulses in the attached neurons which are sent to the auditory nerve and then to the auditory cortex in the brain. The ear starts to develop as early as in the sixth week of pregnancy.
153 Hearing Audition Hearing Hearing or audition is the transduction of sound waves into a neural signal that is made possible by the structures of the ear Figure 1531The large fleshy structure on the lateral aspect of the head is known as the auricleSome sources will also refer to this structure as the pinna though that term is more appropriate for a structure that can be. Ear 17133-160 The most obvious symptom of cochlear hearing. Describe the role of the cochlea in hearing The cochlea is lined with tiny hair from BIOLOGY COLLEGE PREP PART 2 SC052 at James Madison High School.
The cochlea has a very important function in the hearing process. The cochlea which contains many thousands of sensory cells called hair cells is connected to the central hearing system by the hearing or auditory nerve. It takes proper training to interpret sound using a cochlear implant.
It forms a cone approximately 9 mm 035 inch in diameter at its base and. The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. Those closer to the center detect lower-pitched sounds such as a large dog barking.
This occurs at the organ of Corti a structure consisting of tiny hairs throughout the cochlea that vibrate and send electrical signals through the nervous system. Digital signal processing to enhance spectral contrast may be of some help in compensating for the effects of reduced frequency selectivity. The function of the cochlea is to transform the vibrations of the cochlear liquids and associated structures into a neural signal.
As the hair cells move up and down microscopic hair-like projections known as stereocilia that perch on top of the hair cells bump against an overlying structure and bend. As the fluid moves 25000 nerve endings are set into motion. These nerve endings transform the vibrations into electrical impulses that then travel.
A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti the sensory organ of hearing which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea. The cochlea basically takes the vibrations from the sounds we hear and turns it into liquids which causes the stereo cilia to move and cause vibrations that are sent to the brain to be interpreted. The function of the cochlea is to transform the vibrations of the cochlear liquids and associated structures into a.
Hair cells near the wide end of the snail-shaped cochlea detect higher-pitched sounds such as an infant crying. The vestibular system and the cochlea are located in this labyrinth. It converts the auditory signals to neural impulses which are carried by the afferent nerves fibres and auditory nerves to the brain where it is integrated and we hear the sound.
The human cochlea allows the perception of sounds between 20 Hz and 20 000 Hz nearly 10 octaves with a resolution of 1230 octave from 3 Hz at 1000 Hz. Describe the role of the cochlea in hearing. At 1000 Hz the cochlea encodes acoustic pressures between 0 dB SPL 2 x 10-5 Pa and 120 dB.
Explore the inner ear and learn how we hear sounds as related to the cochlea. The auditory nerve feeds this coded message which contains all of the sounds attributes. The sound waves enter the inner ear and then into the cochlea a snail-shaped organ.
The cochlea is a spiral tube that is coiled two and one-half turns around a hollow central pillar the modiolus. The cochlea is filled with a fluid that moves in response to the vibrations from the oval window.

Functions Of An Ear Inner Ear Parts And Functions Structure And Function Of Inner Ear Human Ear Diagram Human Ear Ear Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment